Customize Airflow DAGs
This guide explains how to configure Starlake DAG generation for Apache Airflow. It covers BashOperator and Cloud Run factory classes, Jinja2 template customization, data-aware scheduling with Airflow Datasets, user-defined macros, and Terraform integration. Both inline dependency and data-aware scheduling strategies are described.
Quick start
- Install prerequisites -- Apache Airflow 2.4.0+, starlake-airflow 0.1.2.1+, and starlake 1.0.1+.
- Choose a factory class -- Use
StarlakeAirflowBashJobfor on-premise orStarlakeAirflowCloudRunJobfor GCP Cloud Run. - Configure DAG YAML -- Create a configuration file in
metadata/dagswith template, filename, and options (pre_load_strategy,run_dependencies_first). - Customize templates if needed -- Extend Jinja2 templates for transform parameters, user-defined macros, or Terraform variable injection.
- Generate and deploy -- Run
starlake dag-generate --clean, then copy DAG files to your Airflow DAGs folder.
For general DAG configuration concepts (references, properties, options), see the Customizing DAG Generation hub page. For a hands-on introduction, see the Orchestration Tutorial.
Prerequisites
- Apache Airflow: 2.4.0 or higher (2.6.0 or higher recommended with Cloud Run)
- starlake-airflow: 0.1.2.1 or higher
- starlake: 1.0.1 or higher
Concrete factory classes
Each concrete factory class extends ai.starlake.airflow.StarlakeAirflowJob and implements the sl_job method to generate the Airflow task that runs the corresponding Starlake command.
Default pool
For all templates that instantiate StarlakeAirflowJob, the default_pool option defines the Airflow pool used for all tasks in the DAG.
dag:
options:
default_pool: "custom_default_pool"
#...
StarlakeAirflowBashJob
ai.starlake.airflow.bash.StarlakeAirflowBashJob is a concrete implementation that generates tasks using airflow.operators.bash.BashOperator. Use it for on-premise execution.
An additional SL_STARLAKE_PATH option specifies the path to the Starlake executable.
StarlakeAirflowCloudRunJob
ai.starlake.airflow.gcp.StarlakeAirflowCloudRunJob overrides the sl_job method to run Starlake commands by executing Cloud Run jobs.
Additional options for the Cloud Run job:
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| cloud_run_project_id | str | The optional Cloud Run project id (defaults to the project id of the Composer environment) |
| cloud_run_job_name | str | The required name of the Cloud Run job |
| cloud_run_region | str | The optional region (europe-west1 by default) |
| cloud_run_async | bool | Run the Cloud Run job asynchronously (True by default) |
| retry_on_failure | bool | Retry the Cloud Run job on failure (False by default) |
| retry_delay_in_seconds | int | Delay in seconds before retrying (10 by default) |
When the execution is asynchronous, an ai.starlake.airflow.gcp.CloudRunJobCompletionSensor (extending airflow.sensors.bash.BashSensor) waits for the Cloud Run job to complete.
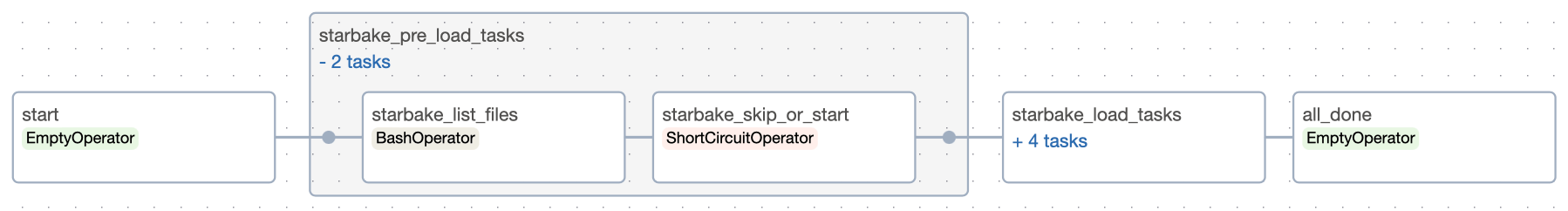
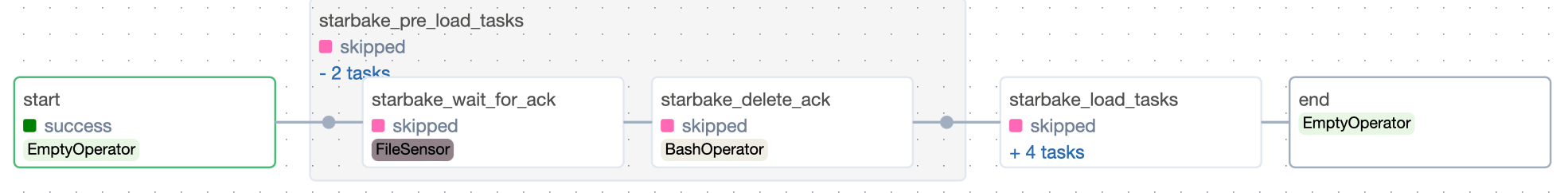
Pre-load strategy visualizations
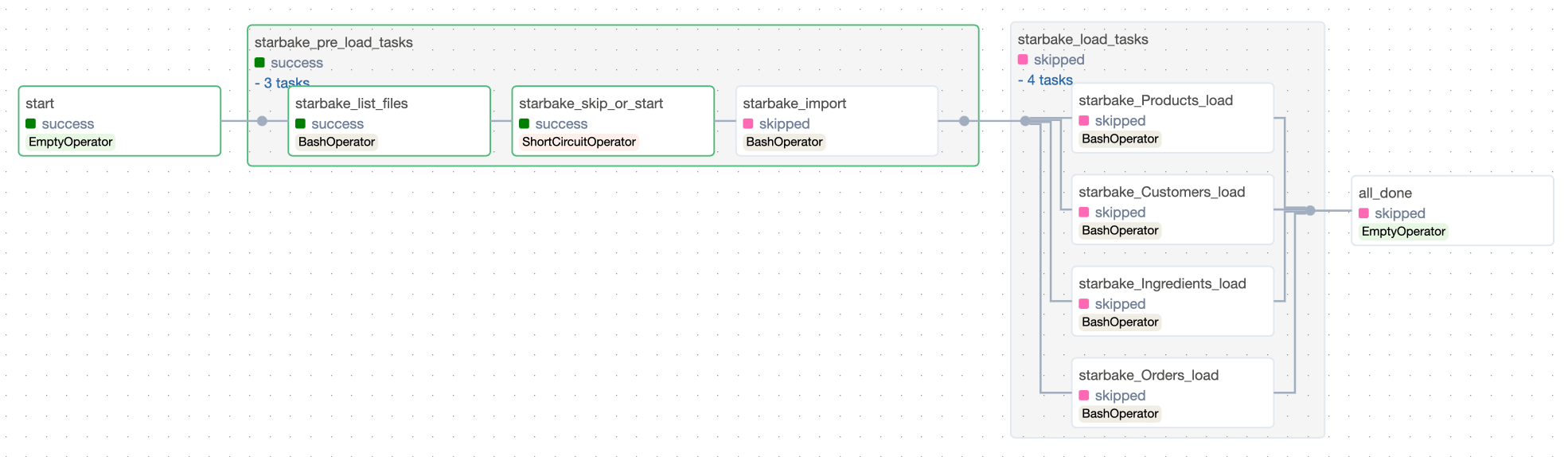
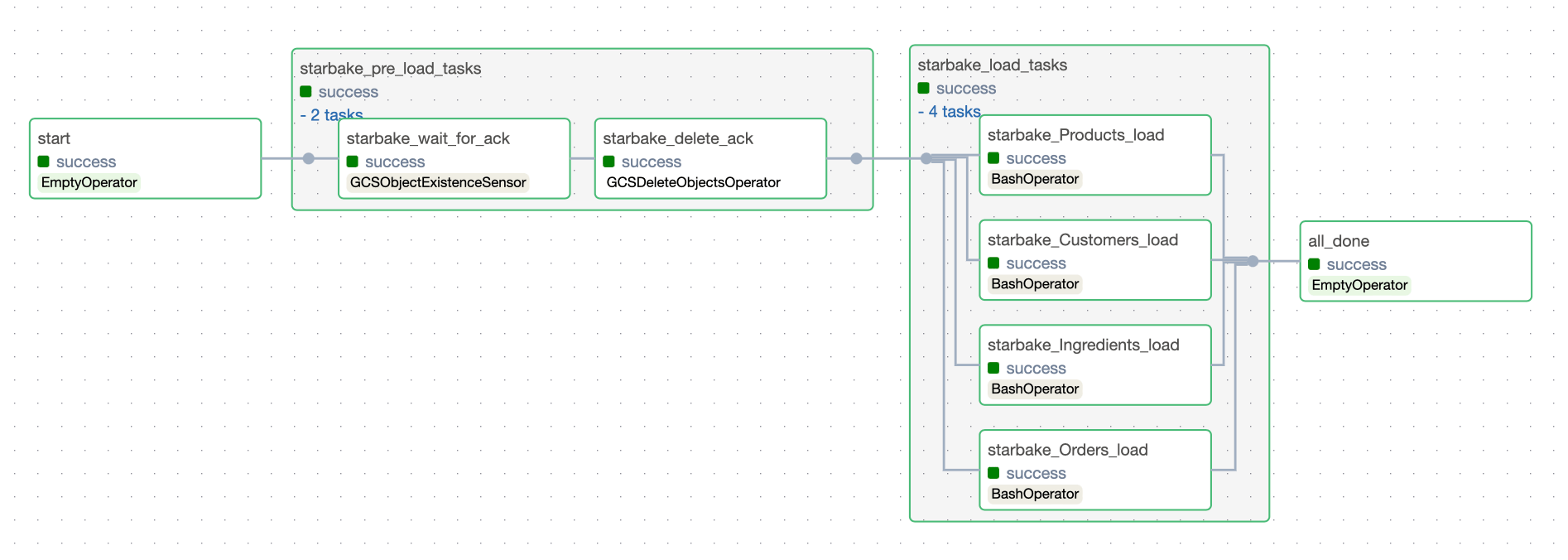
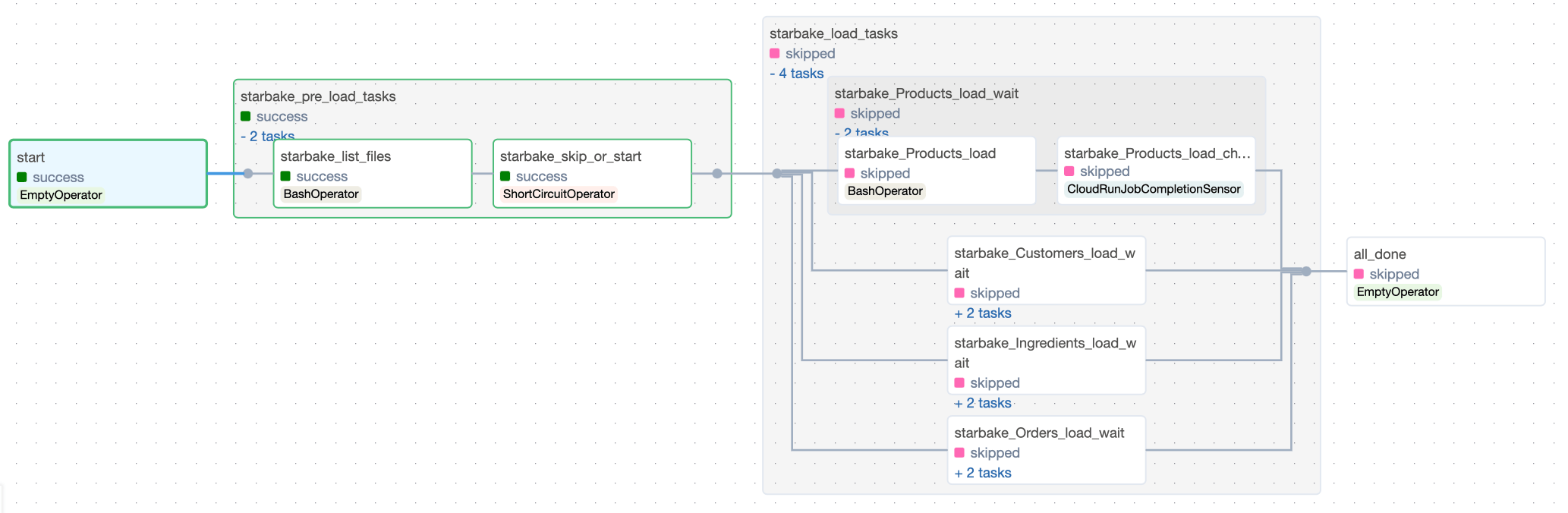
The pre-load strategy options (NONE, IMPORTED, PENDING, ACK) are described in the hub page. Below are the Airflow-specific DAG visualizations for each strategy.
NONE
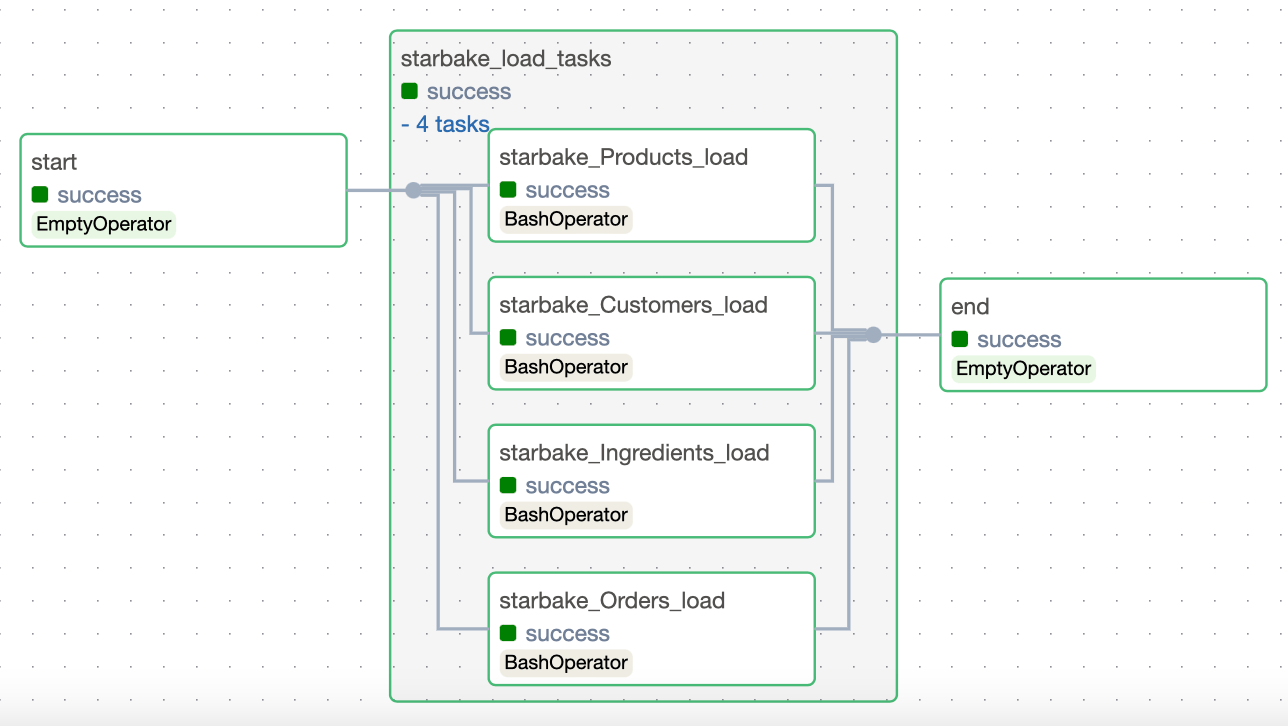
IMPORTED
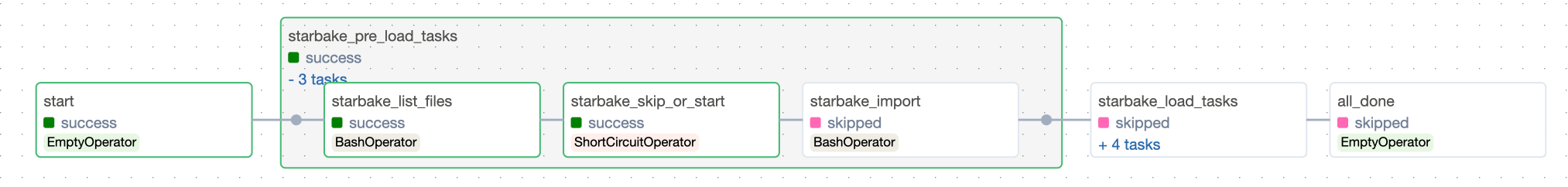
PENDING
ACK
Templates
Data loading templates
__airflow_scheduled_table_tpl.py.j2 is the abstract template for data loading DAGs. It requires a concrete factory class that implements ai.starlake.airflow.StarlakeAirflowJob.
Three Airflow concrete templates extend this abstract template using include statements:
- airflow_scheduled_table_bash.py.j2 -- Instantiates
StarlakeAirflowBashJob:
# This template executes individual bash jobs and requires the following dag generation options set:
# - SL_STARLAKE_PATH: the path to the starlake executable [OPTIONAL]
# ...
{% include 'templates/dags/__starlake_airflow_bash_job.py.j2' %}
{% include 'templates/dags/load/__airflow_scheduled_table_tpl.py.j2' %}
- airflow_scheduled_table_cloud_run.py.j2 -- Instantiates
StarlakeAirflowCloudRunJob:
# This template executes individual cloud run jobs and requires the following dag generation options set:
# - cloud_run_project_id: the project id where the job is located (if not set, the project id of the composer environment will be used) [OPTIONAL]
# - cloud_run_region: the region where the job is located (if not set, europe-west1 will be used) [OPTIONAL]
# - cloud_run_job_name: the name of the job to execute [REQUIRED]
# ...
{% include 'templates/dags/__starlake_airflow_cloud_run_job.py.j2' %}
{% include 'templates/dags/load/__airflow_scheduled_table_tpl.py.j2' %}
Data transformation templates
__airflow_scheduled_task_tpl.py.j2 is the abstract template for data transformation DAGs. It follows the same pattern.
Three Airflow concrete templates exist:
- airflow_scheduled_task_bash.py.j2 -- Instantiates
StarlakeAirflowBashJob:
# ...
{% include 'templates/dags/__starlake_airflow_bash_job.py.j2' %}
{% include 'templates/dags/transform/__airflow_scheduled_task_tpl.py.j2' %}
- airflow_scheduled_task_cloud_run.py.j2 -- Instantiates
StarlakeAirflowCloudRunJob:
# ...
{% include 'templates/dags/__starlake_airflow_cloud_run_job.py.j2' %}
{% include 'templates/dags/transform/__airflow_scheduled_task_tpl.py.j2' %}
Customize existing templates
Built-in options cover most use cases, but some situations require dynamic runtime customization.
Inject transform parameters
Data transformations often require parameterized SQL queries whose parameters are evaluated at runtime.
-- ...
step1 as(
SELECT * FROM step0
# highlight-next-line
WHERE DAT_EXTRACTION >= '{{date_param_min}}' and DAT_EXTRACTION <= '{{date_param_max}}'
)
-- ...
The jobs variable
All Starlake DAG templates for data transformation support a dictionary-like Python variable named jobs. Each key is a transformation name and its value contains the parameters to pass. These entries are added to the corresponding DAG options.
#...
#optional variable jobs as a dict of all parameters to apply by job
#eg jobs = {"task1 domain.task1 name": {"options": "task1 transform options"}, "task2 domain.task2 name": {"options": "task2 transform options"}}
sl_job = StarlakeAirflowCloudRunJob(options=dict(options, **sys.modules[__name__].__dict__.get('jobs', {})))
#...
def sl_transform(self, task_id: str, transform_name: str, transform_options: str=None, spark_config: StarlakeSparkConfig=None, **kwargs) -> T:
"""Transform job.
Generate the scheduler task that will run the starlake `transform` command.
Args:
task_id (str): The optional task id.
transform_name (str): The transform to run.
transform_options (str): The optional transform options to use.
spark_config (StarlakeSparkConfig): The optional spark configuration to use.
Returns:
T: The scheduler task.
"""
task_id = f"{transform_name}" if not task_id else task_id
arguments = ["transform", "--name", transform_name]
transform_options = transform_options if transform_options else self.__class__.get_context_var(transform_name, {}, self.options).get("options", "")
if transform_options:
arguments.extend(["--options", transform_options])
return self.sl_job(task_id=task_id, arguments=arguments, spark_config=spark_config, **kwargs)
#...
Because jobs must be defined in the same module as the generated DAG, create a custom DAG template that extends an existing one:
#...
jobs = #...
#...
{% include 'dags/templates/__custom_jobs.py.j2' %} # our custom code
{% include 'templates/dags/transform/airflow_scheduled_task_cloud_run.py.j2' %} # the template to extend
Airflow user-defined macros
SQL parameters may depend on Airflow context variables. Their evaluation can rely on Airflow user-defined macros.
All Starlake DAG templates for transformation support a dictionary-like Python variable named user_defined_macros:
#...
# [START instantiate_dag]
with DAG(dag_id=os.path.basename(__file__).replace(".py", "").replace(".pyc", "").lower(),
schedule_interval=None if cron == "None" else cron,
schedule=schedule,
default_args=sys.modules[__name__].__dict__.get('default_dag_args', DEFAULT_DAG_ARGS),
catchup=False,
user_defined_macros=sys.modules[__name__].__dict__.get('user_defined_macros', None),
user_defined_filters=sys.modules[__name__].__dict__.get('user_defined_filters', None),
tags=set([tag.upper() for tag in tags]),
description=description) as dag:
#...
Define user_defined_macros in the same module as the generated DAG using a custom template:
from custom import get_days_interval,get_month_periode_depending_on_start_day_params
user_defined_macros = {
"days_interval": get_days_interval,
"month_periode_depending_on_start_day": get_month_periode_depending_on_start_day_params
}
#...
{% include 'dags/templates/__custom_jobs.py.j2' %} # relative to the project metadata folder
{% include 'templates/dags/transform/airflow_scheduled_task_cloud_run.py.j2' %} # relative to src/main/resources starlake resource directory
Terraform integration
A recommended practice is to inject variables using Terraform:
#...
import json
jobs = json.loads("""${jobs}""")
- variables.tf
variable "jobs" {
type = list(object({
name = string
options = string
}))
default = []
}
- main.tf
locals {
jobs = tomap({
for job in var.jobs :
"${job.name}" => {options=job.options}
})
#...
}
resource "google_storage_bucket_object" "composer_storage_objects" {
for_each = local.composer_storage_objects
name = each.value
content = templatefile(
"${path.module}/${each.value}",
merge(local.composer_storage_variables, {jobs=jsonencode(local.jobs)}, {clusters=jsonencode(var.clusters)})
)
bucket = var.composer_bucket
}
- vars_dev.tfvars
jobs = [
{
name = "Products.TopSellingProducts"
options = "{{ days_interval(data_interval_end | ds, var.value.get('TOP_SELLING_PRODUCTS_DELTA', '30')) }}"
},
...
{
name = "Products.MonthlySalesPerProduct"
options = "{{ month_periode_depending_on_start_day(data_interval_end | ds, var.value.get('SALES_PER_PRODUCT_START_DAY', '1')) }}"
}
]
Define a specific DAG configuration that references the custom template:
---
dag:
comment: "agregation dag for domain {\{domain\}} with cloud run" # will appear as a description of the dag
template: "custom_scheduled_task_cloud_run.py.j2" # the dag template to use
filename: "{\{domain\}}_agr_cloud_run.py" # the relative path to the outputDir specified as a parameter of the `dag-generate` command where the generated dag file will be copied
options:
sl_env_var: "{\"SL_ROOT\": \"${root_path}\", \"SL_DATASETS\": \"${root_path}/datasets\", \"SL_TIMEZONE\": \"Europe/Paris\"}"
cloud_run_project_id: "${project_id}"
cloud_run_job_name: "${job_name}-transform" # cloud run job name for auto jobs
cloud_run_job_region: "${region}"
cloud_run_async: False # whether or not to use asynchronous cloud run job execution
# retry_on_failure: True # when asynchronous job execution has been selected, it specifies whether or not we want to use a bash sensor with automatic retry for a specific exit code (implies airflow v2.6+)
tags: "{\{domain\}} {\{domain\}}_CLOUD_RUN" # tags that will be added to the dag
run_dependencies_first: False # whether or not to add all dependencies as airflow tasks within the resulting dag
default_pool: "custom_default_pool" # pool to use for all tasks defined within the dag
- main.tf
resource "google_storage_bucket_object" "composer_storage_objects" {
for_each = local.composer_storage_objects
name = each.value
content = templatefile(
"${path.module}/${each.value}",
merge(local.composer_storage_variables, {jobs=jsonencode(local.jobs)}, {clusters=jsonencode(var.clusters)})
)
bucket = var.composer_bucket
}
Dependencies
Starlake calculates all dependencies for each transformation by analyzing SQL queries.
The run_dependencies_first option controls whether dependencies are generated inline or handled through Airflow's data-aware scheduling (default: False).
All dependencies are available in the generated DAG via the Python dictionary variable task_deps:
task_deps=json.loads("""[ {
"data" : {
"name" : "Customers.HighValueCustomers",
"typ" : "task",
"parent" : "Customers.CustomerLifeTimeValue",
"parentTyp" : "task",
"parentRef" : "CustomerLifetimeValue",
"sink" : "Customers.HighValueCustomers"
},
"children" : [ {
"data" : {
"name" : "Customers.CustomerLifeTimeValue",
"typ" : "task",
"parent" : "starbake.Customers",
"parentTyp" : "table",
"parentRef" : "starbake.Customers",
"sink" : "Customers.CustomerLifeTimeValue"
},
"children" : [ {
"data" : {
"name" : "starbake.Customers",
"typ" : "table",
"parentTyp" : "unknown"
},
"task" : false
}, {
"data" : {
"name" : "starbake.Orders",
"typ" : "table",
"parentTyp" : "unknown"
},
"task" : false
} ],
"task" : true
} ],
"task" : true
} ]""")
Inline dependencies
With run_dependencies_first = True, all dependencies are included in the same DAG.
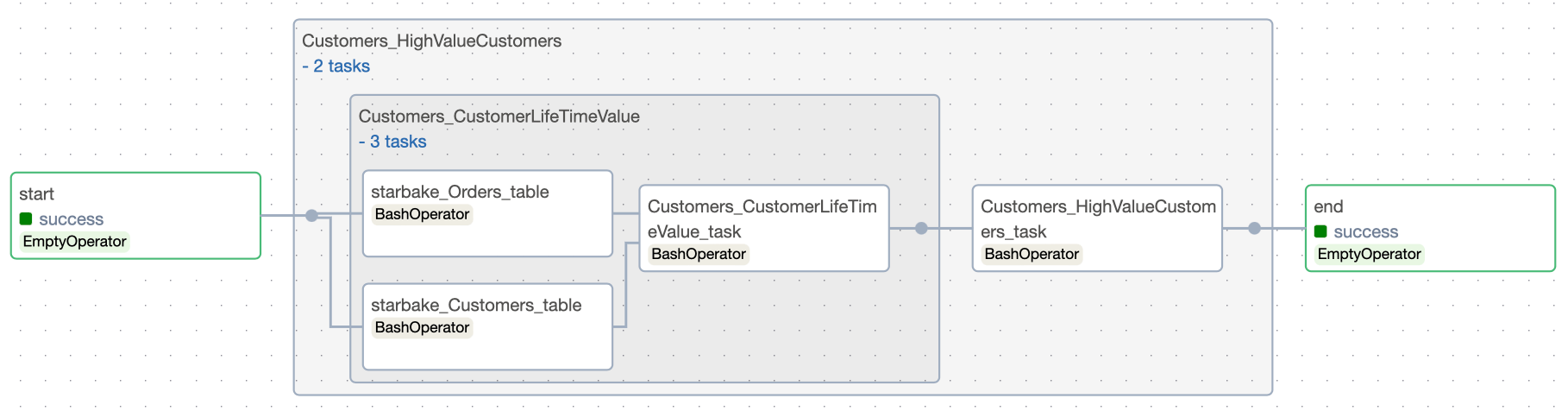
Data-aware scheduling
With run_dependencies_first = False (default), Airflow uses Datasets to trigger the transform DAG when its dependencies are met.
A schedule is created using Airflow Datasets:
#...
schedule = None
datasets: Set[str] = []
_extra_dataset: Union[dict, None] = sys.modules[__name__].__dict__.get('extra_dataset', None)
_extra_dataset_parameters = '?' + '&'.join(list(f'{k}={v}' for (k,v) in _extra_dataset.items())) if _extra_dataset else ''
# if you choose to not load the dependencies, a schedule will be created to check if the dependencies are met
def _load_datasets(task: dict):
if 'children' in task:
for child in task['children']:
datasets.append(keep_ascii_only(child['data']['name']).lower())
_load_datasets(child)
if run_dependencies_first.lower() != 'true':
for task in task_deps:
_load_datasets(task)
schedule = list(map(lambda dataset: Dataset(dataset + _extra_dataset_parameters), datasets))
#...
with DAG(dag_id=os.path.basename(__file__).replace(".py", "").replace(".pyc", "").lower(),
schedule_interval=None if cron == "None" else cron,
schedule=schedule,
default_args=sys.modules[__name__].__dict__.get('default_dag_args', DEFAULT_DAG_ARGS),
catchup=False,
user_defined_macros=sys.modules[__name__].__dict__.get('user_defined_macros', None),
user_defined_filters=sys.modules[__name__].__dict__.get('user_defined_filters', None),
tags=set([tag.upper() for tag in tags]),
description=description) as dag:
#...
How Datasets are updated
The ai.starlake.airflow.StarlakeAirflowJob class records outlets for each Starlake command:
def __init__(
self,
pre_load_strategy: Union[StarlakePreLoadStrategy, str, None],
options: dict=None,
**kwargs) -> None:
#...
self.outlets: List[Dataset] = kwargs.get('outlets', [])
def sl_import(self, task_id: str, domain: str, **kwargs) -> BaseOperator:
#...
dataset = Dataset(keep_ascii_only(domain).lower())
self.outlets += kwargs.get('outlets', []) + [dataset]
#...
def sl_load(
self,
task_id: str,
domain: str,
table: str,
spark_config: StarlakeSparkConfig=None,
**kwargs) -> BaseOperator:
#...
dataset = Dataset(keep_ascii_only(f'\{domain\}.\{table\}').lower())
self.outlets += kwargs.get('outlets', []) + [dataset]
#...
def sl_transform(
self,
task_id: str,
transform_name: str,
transform_options: str=None,
spark_config: StarlakeSparkConfig=None,
**kwargs) -> BaseOperator:
#...
dataset = Dataset(keep_ascii_only(transform_name).lower())
self.outlets += kwargs.get('outlets', []) + [dataset]
#...
All recorded outlets are used at the last step of the DAG to update the Datasets:
end = sl_job.dummy_op(task_id="end", outlets=[Dataset(keep_ascii_only(dag.dag_id))]+list(map(lambda x: Dataset(x.uri + _extra_dataset_parameters), sl_job.outlets)))
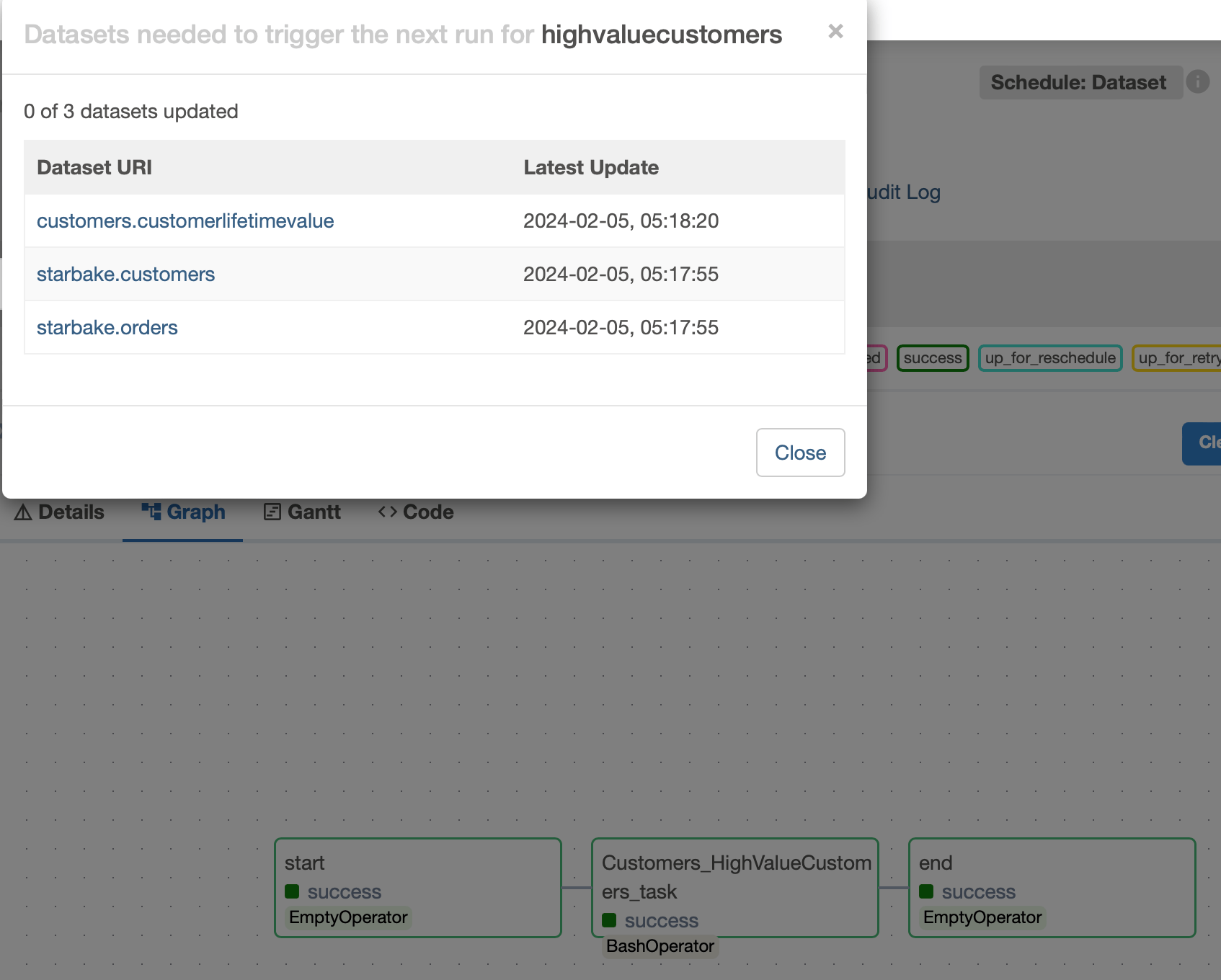
The outlets property enables effortless scheduling of transform DAGs in conjunction with Starlake DAG generation.
Frequently Asked Questions
How does Starlake generate Airflow tasks?
Starlake uses concrete factory classes that inherit from StarlakeAirflowJob. The StarlakeAirflowBashJob class generates BashOperator tasks for on-premise execution. The StarlakeAirflowCloudRunJob class generates Cloud Run tasks.
What version of Airflow is required?
Apache Airflow 2.4.0 minimum. Airflow 2.6.0 or higher is recommended for Cloud Run integration.
How does data-aware scheduling work with Starlake?
When run_dependencies_first is False (default), Starlake generates Airflow Datasets for each load and transform. The transformation DAG only executes when all its dependencies have been materialized.
What is the difference between inline and data-aware scheduling?
In inline mode (run_dependencies_first=True), all dependencies are included in the same DAG. In data-aware mode (run_dependencies_first=False), the DAG is triggered by Airflow when dependent Datasets are updated.
How to pass dynamic SQL parameters at runtime?
Define a Python variable jobs in a custom Jinja2 template. Each key represents a transformation name and its value contains the parameters to pass.
How to integrate Starlake DAGs with Terraform?
Use Terraform variables to inject the jobs parameters into templates via templatefile(). Deploy the DAG files to the Composer bucket with google_storage_bucket_object.
Can I define a specific Airflow pool?
Yes. The default_pool option in the DAG configuration defines the Airflow pool used for all tasks in the DAG.
How does asynchronous Cloud Run execution work?
If cloud_run_async is True (default), a CloudRunJobCompletionSensor is instantiated to wait for the completion of the Cloud Run job execution.