Customize Dagster DAGs
This guide covers Dagster-specific customization for Starlake DAG generation. It details Shell and Cloud Run factory classes, Jinja2 templates for data loading and transformation, and the Multi Asset Sensor mechanism for dependency-driven execution. It explains how Dagster asset materialization integrates with Starlake commands.
Quick start
- Install prerequisites -- Dagster 1.6.0+, starlake-dagster 0.1.2+, and starlake 1.0.1+.
- Choose a factory class -- Use
StarlakeDagsterShellJobfor local/on-premise orStarlakeDagsterCloudRunJobfor GCP Cloud Run. - Configure DAG YAML -- Create a configuration file in
metadata/dagswith the Dagster template, filename, and options (run_dependencies_first). - Generate and deploy -- Run
starlake dag-generate --clean, then deploy the generated files to your Dagster repository.
For general DAG configuration concepts (references, properties, options), see the Customizing DAG Generation hub page. For a hands-on introduction, see the Orchestration Tutorial.
Prerequisites
- Dagster: 1.6.0 or higher
- starlake-dagster: 0.1.2 or higher
- starlake: 1.0.1 or higher
Concrete factory classes
Each concrete factory class extends ai.starlake.dagster.StarlakeDagsterJob and implements the sl_job method to generate the Dagster op that runs the corresponding Starlake command.
StarlakeDagsterShellJob
ai.starlake.dagster.shell.StarlakeDagsterShellJob generates nodes using the dagster-shell library. Use it for on-premise or local execution.
An additional SL_STARLAKE_PATH option specifies the path to the Starlake executable.
StarlakeDagsterCloudRunJob
ai.starlake.dagster.gcp.StarlakeDagsterCloudRunJob overrides the sl_job method to run Starlake commands by executing Cloud Run jobs.
Additional options for the Cloud Run job:
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| cloud_run_project_id | str | The optional Cloud Run project id (defaults to the current GCP project id) |
| cloud_run_job_name | str | The required name of the Cloud Run job |
| cloud_run_region | str | The optional region (europe-west1 by default) |
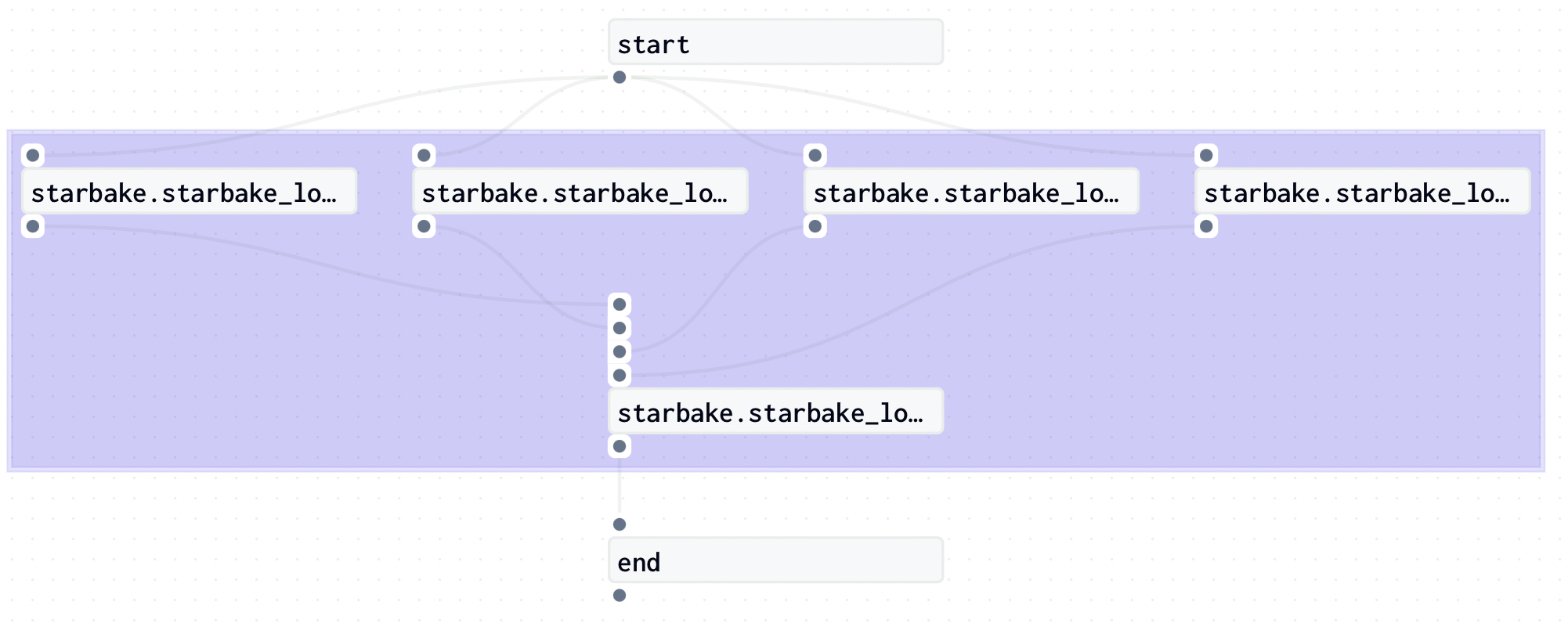
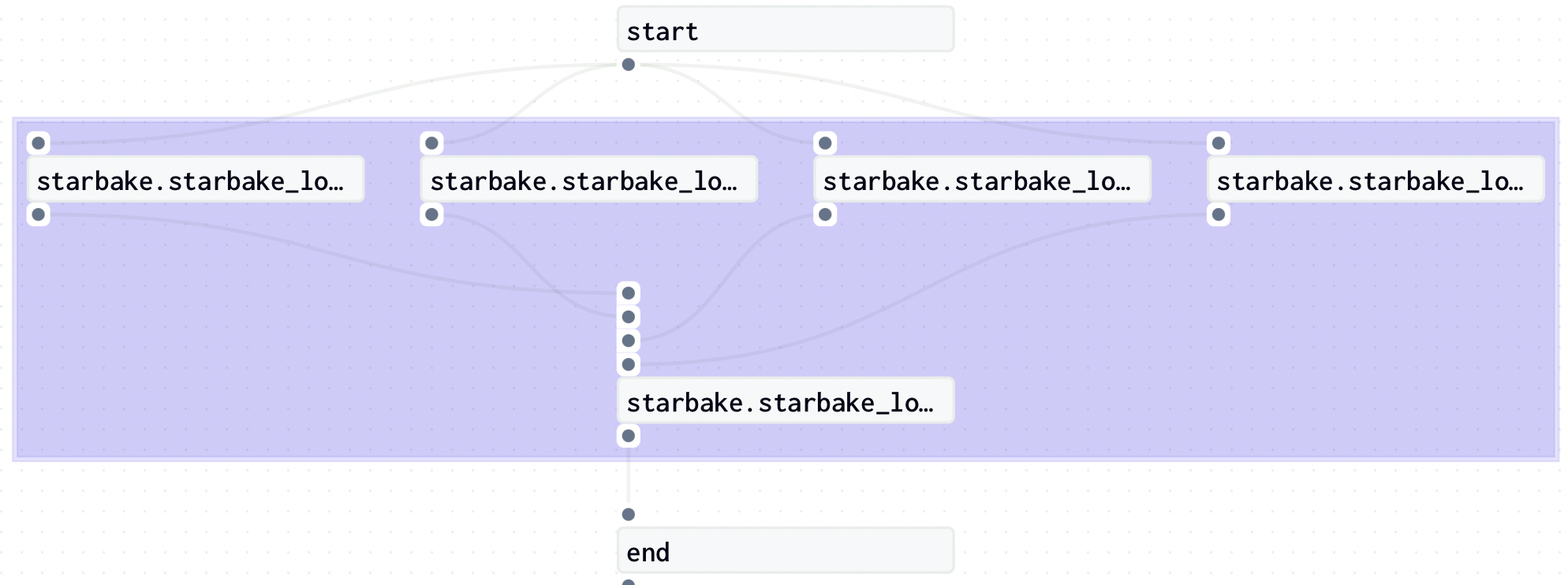
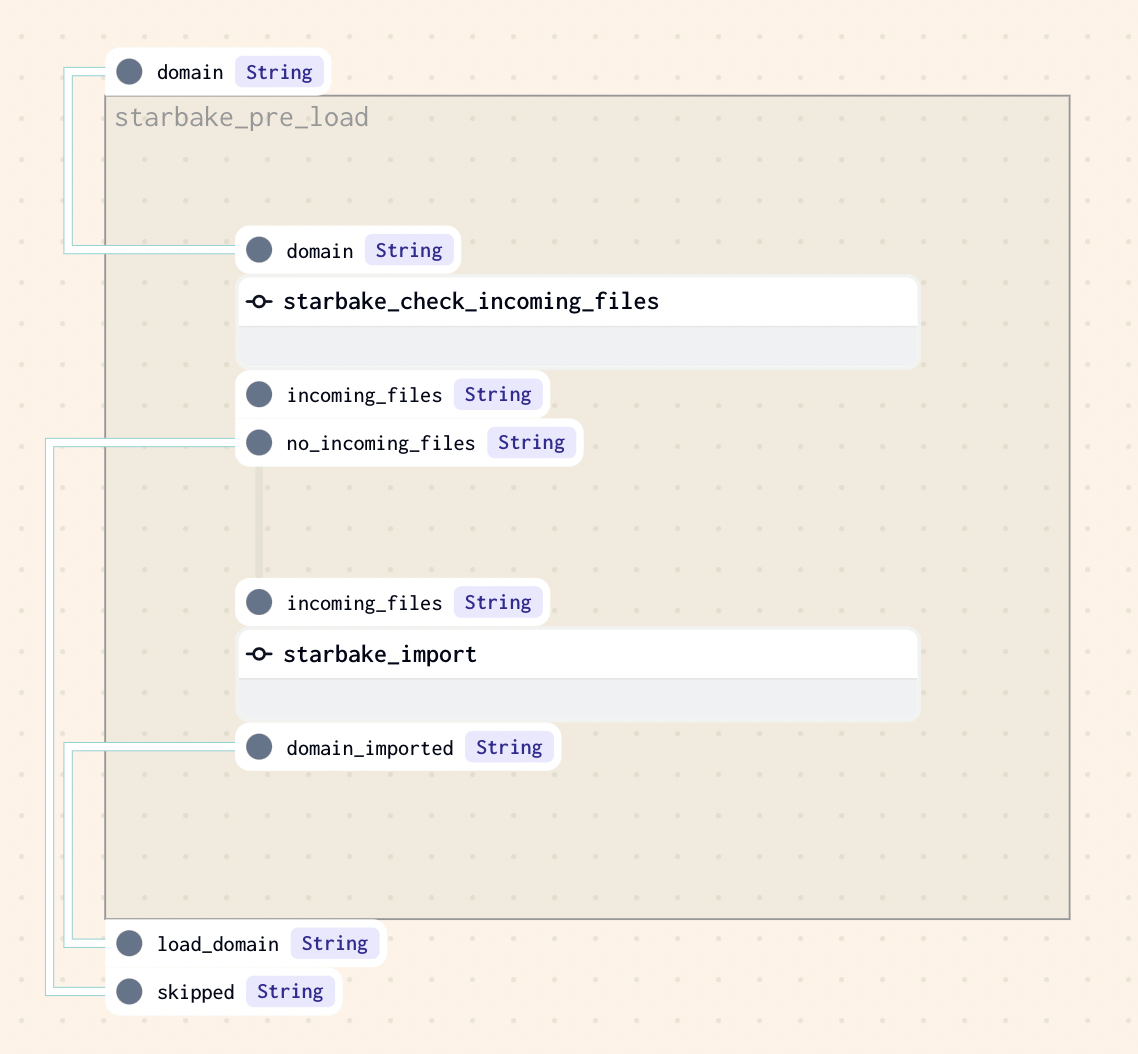
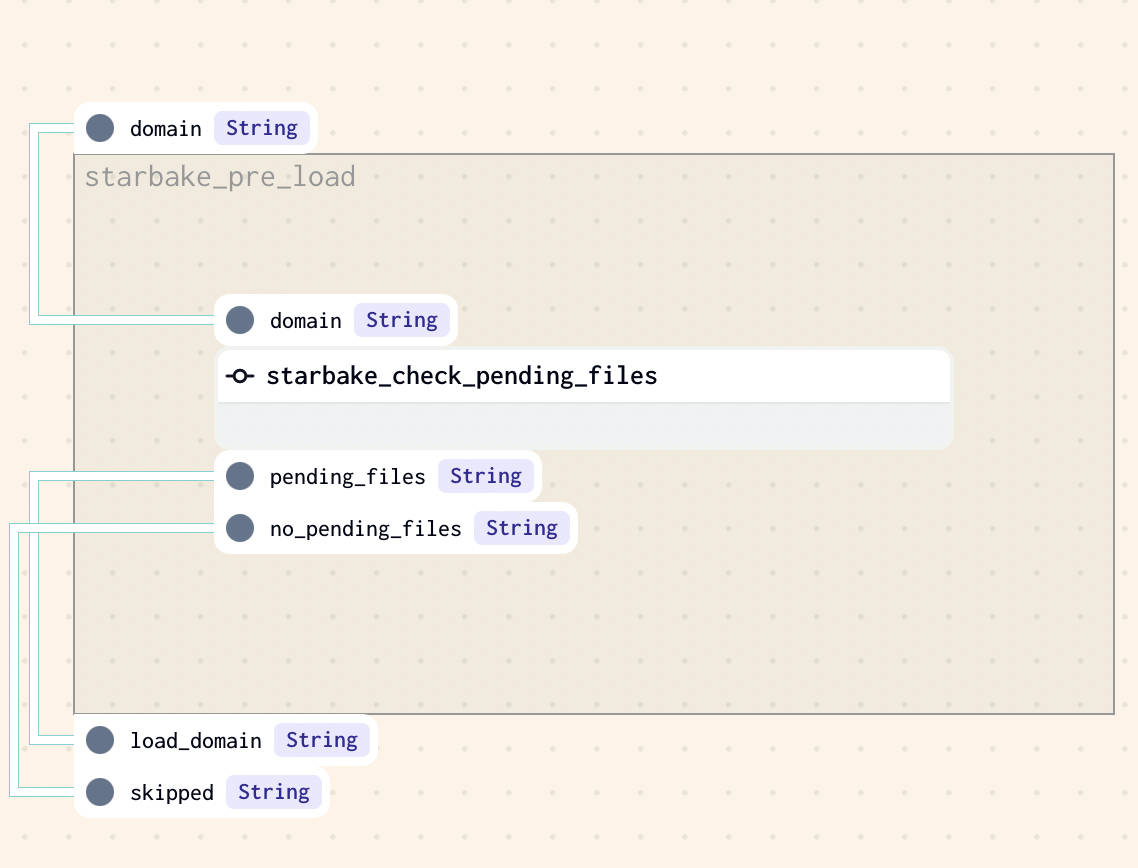
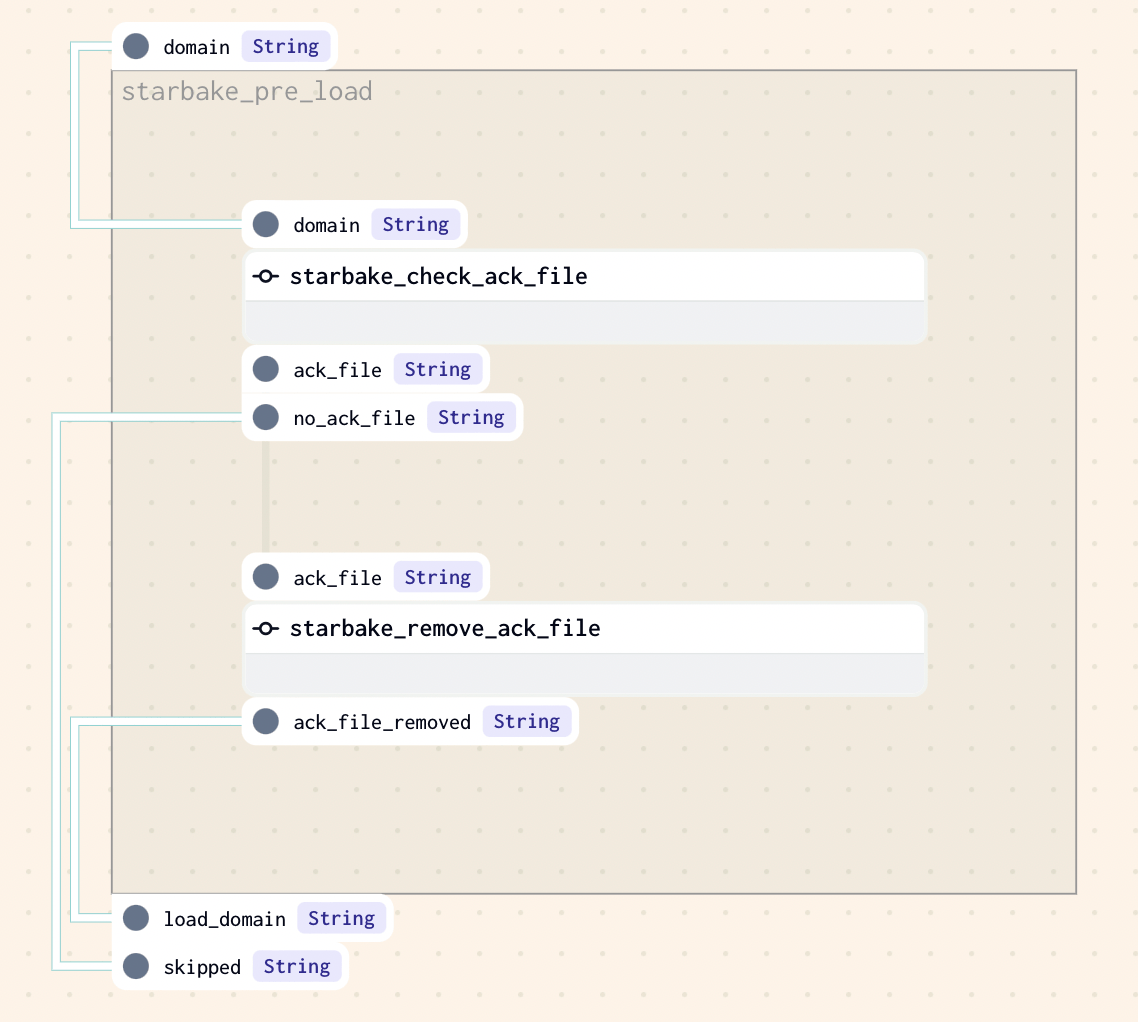
Pre-load strategy visualizations
The pre-load strategy options (NONE, IMPORTED, PENDING, ACK) are described in the hub page. Below are the Dagster-specific visualizations for each strategy.
NONE
IMPORTED
PENDING
ACK
Templates
Data loading templates
__dagster_scheduled_table_tpl.py.j2 is the abstract template for Dagster data loading DAGs. It requires a concrete factory class implementing ai.starlake.dagster.StarlakeDagsterJob.
Three Dagster concrete templates extend it using include statements:
- dagster_scheduled_table_shell.py.j2 -- Instantiates
StarlakeDagsterShellJob:
# This template executes individual shell jobs and requires the following dag generation options set:
# - SL_STARLAKE_PATH: the path to the starlake executable [OPTIONAL]
# ...
{% include 'templates/dags/__starlake_dagster_shell_job.py.j2' %}
{% include 'templates/dags/load/__dagster_scheduled_table_tpl.py.j2' %}
- dagster_scheduled_table_cloud_run.py.j2 -- Instantiates
StarlakeDagsterCloudRunJob:
# This template executes individual cloud run jobs and requires the following dag generation options set:
# - cloud_run_project_id: the project id where the job is located (if not set, the current GCP project id will be used) [OPTIONAL]
# - cloud_run_region: the region where the job is located (if not set, europe-west1 will be used) [OPTIONAL]
# - cloud_run_job_name: the name of the job to execute [REQUIRED]
# ...
{% include 'templates/dags/__starlake_dagster_cloud_run_job.py.j2' %}
{% include 'templates/dags/load/__dagster_scheduled_table_tpl.py.j2' %}
Data transformation templates
__dagster_scheduled_task_tpl.py.j2 is the abstract template for data transformation DAGs. It follows the same pattern.
Three Dagster concrete templates exist:
- dagster_scheduled_task_shell.py.j2 -- Instantiates
StarlakeDagsterShellJob:
# ...
{% include 'templates/dags/__starlake_dagster_shell_job.py.j2' %}
{% include 'templates/dags/transform/__dagster_scheduled_task_tpl.py.j2' %}
- dagster_scheduled_task_cloud_run.py.j2 -- Instantiates
StarlakeDagsterCloudRunJob:
# ...
{% include 'templates/dags/__starlake_dagster_cloud_run_job.py.j2' %}
{% include 'templates/dags/transform/__dagster_scheduled_task_tpl.py.j2' %}
Dependencies
Starlake calculates all dependencies for each transformation by analyzing SQL queries.
The run_dependencies_first option controls whether dependencies are generated inline or handled through the Dagster Multi Asset Sensor mechanism (default: False).
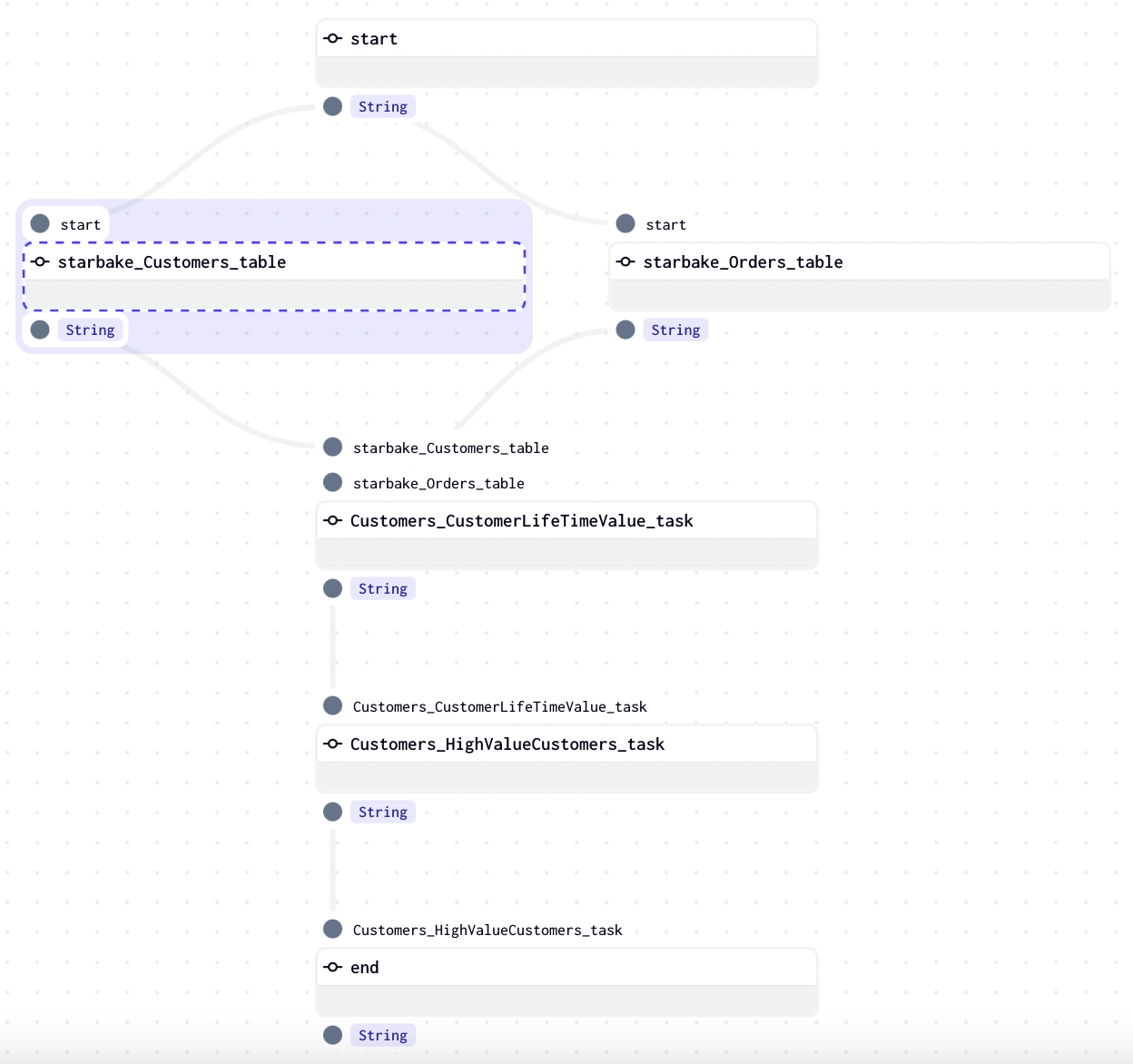
All dependencies are available in the generated DAG via the Python dictionary variable task_deps:
task_deps=json.loads("""[ {
"data" : {
"name" : "Customers.HighValueCustomers",
"typ" : "task",
"parent" : "Customers.CustomerLifeTimeValue",
"parentTyp" : "task",
"parentRef" : "CustomerLifetimeValue",
"sink" : "Customers.HighValueCustomers"
},
"children" : [ {
"data" : {
"name" : "Customers.CustomerLifeTimeValue",
"typ" : "task",
"parent" : "starbake.Customers",
"parentTyp" : "table",
"parentRef" : "starbake.Customers",
"sink" : "Customers.CustomerLifeTimeValue"
},
"children" : [ {
"data" : {
"name" : "starbake.Customers",
"typ" : "table",
"parentTyp" : "unknown"
},
"task" : false
}, {
"data" : {
"name" : "starbake.Orders",
"typ" : "table",
"parentTyp" : "unknown"
},
"task" : false
} ],
"task" : true
} ],
"task" : true
} ]""")
Inline dependencies
With run_dependencies_first = True, all dependencies are included in the same Dagster job.
Multi Asset Sensor
With run_dependencies_first = False (default), a sensor checks whether all dependent assets have been materialized before triggering execution.
#...
from dagster import AssetKey, MultiAssetSensorDefinition, MultiAssetSensorEvaluationContext, SkipReason, Definitions
# if you want to load dependencies, set run_dependencies_first to True in the options
run_dependencies_first: bool = StarlakeDagsterJob.get_context_var(var_name='run_dependencies_first', default_value='False', options=options).lower() == 'true'
sensor = None
# if you choose to not load the dependencies, a sensor will be created to check if the dependencies are met
if not run_dependencies_first:
assets: Set[str] = []
def load_assets(task: dict):
if 'children' in task:
for child in task['children']:
assets.append(sanitize_id(child['data']['name']))
load_assets(child)
for task in task_deps:
load_assets(task)
def multi_asset_sensor_with_skip_reason(context: MultiAssetSensorEvaluationContext):
asset_events = context.latest_materialization_records_by_key()
if all(asset_events.values()):
context.advance_all_cursors()
return RunRequest()
elif any(asset_events.values()):
materialized_asset_key_strs = [
key.to_user_string() for key, value in asset_events.items() if value
]
not_materialized_asset_key_strs = [
key.to_user_string() for key, value in asset_events.items() if not value
]
return SkipReason(
f"Observed materializations for {materialized_asset_key_strs}, "
f"but not for {not_materialized_asset_key_strs}"
)
else:
return SkipReason("No materializations observed")
sensor = MultiAssetSensorDefinition(
name = f'{job_name}_sensor',
monitored_assets = list(map(lambda asset: AssetKey(asset), assets)),
asset_materialization_fn = multi_asset_sensor_with_skip_reason,
minimum_interval_seconds = 60,
description = f"Sensor for {job_name}",
job_name = job_name,
)
#...
defs = Definitions(
jobs=[generate_job()],
schedules=crons,
sensors=[sensor] if sensor else [],
)
How assets are materialized
The ai.starlake.dagster.StarlakeDagsterJob class records assets for each Starlake command:
def sl_import(self, task_id: str, domain: str, **kwargs) -> NodeDefinition:
kwargs.update({'asset': AssetKey(sanitize_id(domain))})
#...
def sl_load(self, task_id: str, domain: str, table: str, spark_config: StarlakeSparkConfig=None, **kwargs) -> NodeDefinition:
kwargs.update({'asset': AssetKey(sanitize_id(f"\{domain\}.\{table\}"))})
#...
def sl_transform(self, task_id: str, transform_name: str, transform_options: str = None, spark_config: StarlakeSparkConfig = None, **kwargs) -> NodeDefinition:
kwargs.update({'asset': AssetKey(sanitize_id(transform_name))})
#...
Each asset is materialized at runtime through the Dagster op defined in sl_job of the concrete factory class:
def sl_job(self, task_id: str, arguments: list, spark_config: StarlakeSparkConfig=None, **kwargs) -> NodeDefinition:
"""Overrides IStarlakeJob.sl_job()
Generate the Dagster node that will run the starlake command.
Args:
task_id (str): The required task id.
arguments (list): The required arguments of the starlake command to run.
Returns:
OpDefinition: The Dagster node.
"""
command = self.__class__.get_context_var("SL_STARLAKE_PATH", "starlake", self.options) + f" {' '.join(arguments)}"
asset_key: AssetKey = kwargs.get("asset", None)
@op(
name=task_id,
ins=kwargs.get("ins", {}),
out={kwargs.get("out", "result"): Out(str)},
)
def job(context, **kwargs):
output, return_code = execute_shell_command(
shell_command=command,
output_logging="STREAM",
log=context.log,
cwd=self.sl_root,
env=self.sl_env_vars,
log_shell_command=True,
)
if return_code:
raise Failure(description=f"Starlake command {command} execution failed with output: {output}")
if asset_key:
yield AssetMaterialization(asset_key=asset_key.path, description=kwargs.get("description", f"Starlake command {command} execution succeeded"))
yield Output(value=output, output_name="result")
return job
Frequently Asked Questions
How does Starlake generate Dagster ops?
Starlake uses concrete factory classes that inherit from StarlakeDagsterJob. StarlakeDagsterShellJob generates ops via the dagster-shell library. StarlakeDagsterCloudRunJob generates ops that execute Cloud Run jobs.
What version of Dagster is required?
Dagster 1.6.0 minimum and starlake-dagster 0.1.2 minimum.
How does Starlake manage dependencies in Dagster?
With run_dependencies_first=True, all dependencies are included inline in the same job. With run_dependencies_first=False (default), a Multi Asset Sensor monitors the materialization of dependent assets before triggering the job.
How does the Starlake Multi Asset Sensor work?
The sensor checks that all dependent assets have been materialized. If so, it triggers a RunRequest. Otherwise, it returns a SkipReason indicating the missing assets.
How are assets materialized?
Each sl_import, sl_load, and sl_transform command registers a corresponding AssetKey. The materialization is performed at execution time via AssetMaterialization in the sl_job method.
What additional options are needed for Cloud Run?
cloud_run_project_id (optional), cloud_run_job_name (required), and cloud_run_region (optional, defaults to europe-west1).
Can I use Dagster locally with Starlake?
Yes. The StarlakeDagsterShellJob template executes Starlake commands locally via shell. You just need to specify the SL_STARLAKE_PATH option.